Trying to conceive but not getting results? You’re not alone. Many women face fertility issues, and one of the lesser-known yet common causes is blocked fallopian tubes. This condition can quietly prevent pregnancy without showing any clear signs. But the good news is, there are ways to diagnose and treat it. In this guide, we’ll explain everything you need to know—from symptoms and causes to the latest treatments.
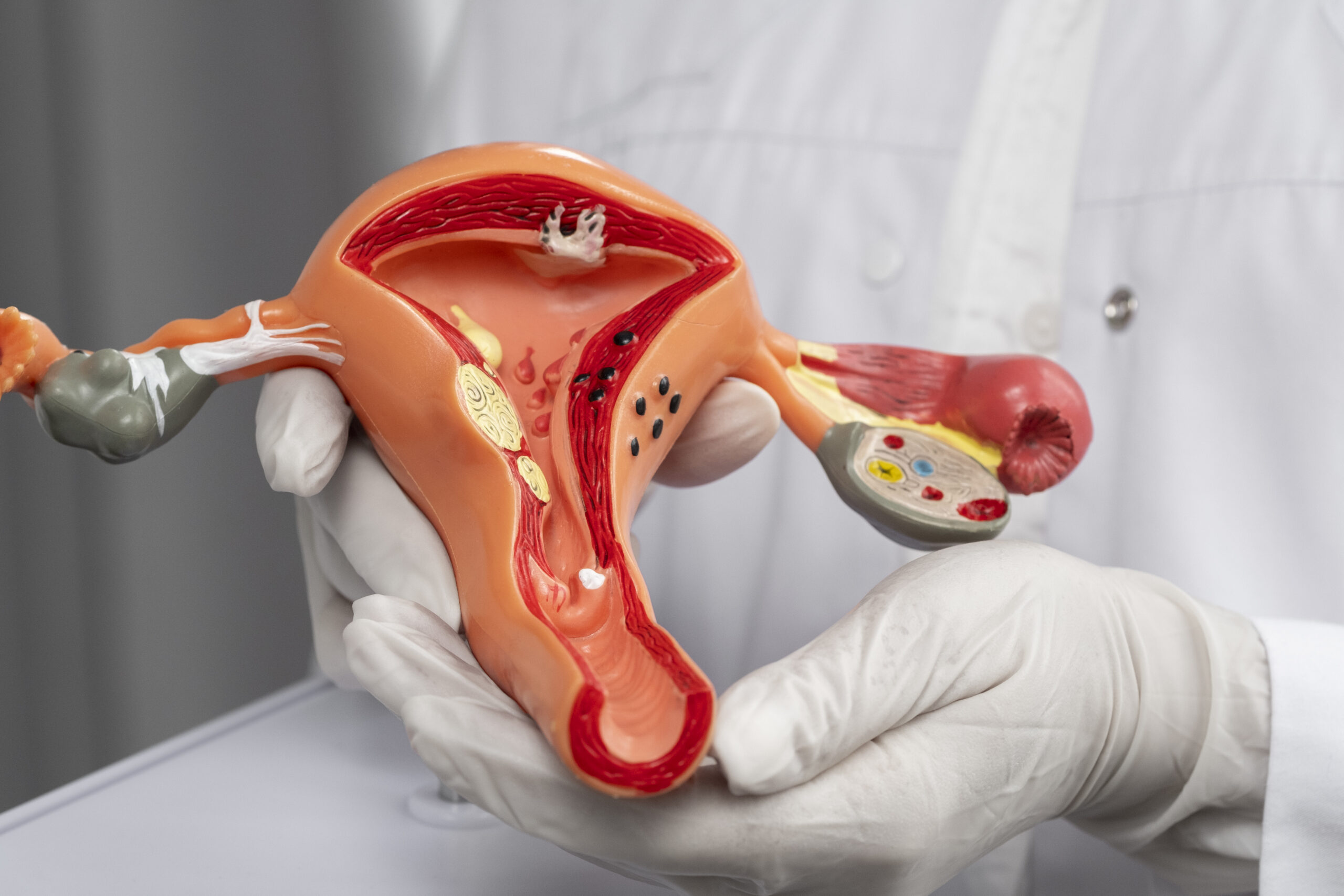
What Are Fallopian Tubes and Why Are They Important?
Fallopian tubes are two thin tubes, one on each side of the uterus. Their job is simple but vital: they carry the egg from the ovary to the uterus. If a sperm meets the egg, fertilization happens in the tube. But if the tubes are blocked, this meeting can’t take place. That means pregnancy becomes difficult or impossible without help.
What Are Blocked Fallopian Tubes?
When we say “blocked fallopian tubes,” we mean that one or both tubes have an obstruction that stops the egg and sperm from meeting. This blockage can happen at any point in the tube and can be partial or complete.
Partial blockages might still allow for some fertility, but complete blockages often require medical treatment or assisted reproductive technologies like IVF. The problem can be hard to detect because it usually doesn’t come with clear symptoms.
What Causes Blocked Fallopian Tubes?
There are several reasons why the fallopian tubes may become blocked:
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): A common cause. This is usually due to untreated infections, often from sexually transmitted diseases.
- Endometriosis: The growth of tissue similar to the uterus lining outside the uterus can affect the tubes.
- Surgery Complications: Past abdominal or pelvic surgeries may lead to scar tissue that causes blockage.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: If you’ve had one before, it might have damaged the tube.
- Fibroids: These can grow near the fallopian tubes and press against them.
- Tubal Ligation Reversal: Women who attempt to reverse permanent birth control may face blockage risks.
Symptoms of Blocked Fallopian Tubes
One of the toughest things about blocked fallopian tubes is that they often don’t show symptoms. Many women only find out when they try to conceive. However, if symptoms do appear, they might include:
- Pain during sex
- Painful periods
- Lower abdominal pain
- Unusual vaginal discharge
- Trouble getting pregnant for over a year
Sometimes, if the tube is filled with fluid (a condition called hydrosalpinx), it may cause swelling and discomfort.
How Are Blocked Fallopian Tubes Diagnosed?
If your doctor suspects blocked tubes, they will usually recommend one or more of these tests:
- Hysterosalpingogram (HSG): A type of X-ray where a dye is injected into the uterus and fallopian tubes to see if they are open.
- Sonohysterography: This uses ultrasound and saline solution to check for blockages.
- Laparoscopy: A small surgical procedure where a camera is inserted into the abdomen to get a closer look at the tubes.
- Blood Tests: To rule out infections or hormonal imbalances.
Getting a proper diagnosis is the first step toward a solution. A skilled gynaecologist will help you choose the right path based on your results.
Treatment Options for Blocked Fallopian Tubes
Treatment depends on how severe the blockage is and what caused it. Here are some common options:
1. Surgery
If the blockage is minor, surgery can sometimes remove the scar tissue and reopen the tubes. This is often done through laparoscopy, which has a quicker recovery time than open surgery.
2. In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
If surgery is not possible or the tubes are severely damaged, IVF is often recommended. It bypasses the fallopian tubes altogether by fertilizing the egg outside the body and placing it directly in the uterus.
3. Treating Underlying Conditions
Sometimes, treating the underlying cause—like an infection or endometriosis—can help improve the chances of pregnancy.
4. Lifestyle Adjustments
Healthy habits can support overall reproductive health. Consider these:
- Eating a balanced diet
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Reducing stress
- Avoiding alcohol and tobacco
While these steps won’t unblock the tubes, they can improve your chances of success with treatment.
When to Seek Help
If you’ve been trying to conceive for more than 12 months (or six months if you’re over 35), it’s time to speak to a specialist. Early testing and diagnosis can save you time and reduce frustration.
For women in Kerala, we recommend visiting Lifeline Hospital, Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology in Kochi. Their experienced team provides advanced diagnostic services and fertility treatments tailored to your needs.
Conclusion
Blocked fallopian tubes can be a major obstacle for women trying to get pregnant, but they’re not the end of the road. With modern medicine, early diagnosis, and the right care, many women go on to have healthy pregnancies. Don’t let silence or uncertainty stop you. If you suspect a problem, reach out to a fertility expert and explore your options. There is hope, and help is available.
FAQs
1. Can I get pregnant naturally with one blocked fallopian tube?
Yes, if one tube is healthy and there are no other fertility issues, natural conception is still possible.
2. Is surgery always required to treat blocked tubes?
Not always. Treatment depends on the cause and severity. IVF is a common alternative to surgery.
3. What are the chances of pregnancy after treating blocked tubes?
Success rates vary, but with IVF or successful surgery, many women conceive within a year.
4. How can I prevent fallopian tube blockages?
Preventing STIs, avoiding pelvic infections, and seeking timely medical care can reduce your risk.
5. Are blocked fallopian tubes painful?
Not always. Some women feel no pain, while others may have pelvic discomfort or painful periods.